Appunto di Anna: capire qual è il nome definitivo di jcricket e riportare qui contenuto di:
The LOD Platform technology enables institutions to embrace the advantages of linked open data. The Cluster Knowledge Base (CKB, or Entity Knowledge Base) is the result of the entity identification and resolution obtained through clustering processes with data coming from different participating libraries with enrichment of external sources. JCricket is the Linked Data Entity Editor developed by the Share-VDE community, a tool designed for collaboratively curating entity data living in the CKB.
The entity editor JCricket opens new forms of cooperation among institutions. The CKB is conceived as a live source of authoritative data: through JCricket editor, member institutions engage in collaborative entity management and in a new way of performing authority control. JCricket is the tool for collaborative linked data entity management. It enables - according to the BIBFRAME ontology - the entity curation (e.g. creation of new entities, entity modification, the application of entity merge and split functions). The scope is to improve the quality of the Entity Knowledge Base that is a live source produced through clustering and daily update processes. JCricket is a manual application that makes it possible to manage bibliography data in the form of entities. It empowers professional librarians to enhance the quality of machine-generated data output of MARC to BIBFRAME transformation.
Also, not only JCricket operates on members' institutions data processed by the the LOD Platform, but it can serve as a bridge with cross-domain contexts to create links with third parties, such as FOLIO community and Wikidata.
JCricket overview
Here follows the high-level description of JCricket functions. All manual functions are also available through corresponding GraphQL APIs.
For more detailed descriptions refer to:
- the user manual, dedicated to professional users (librarians) who will use JCricket for shared cataloguing;
- the UX guide, describing the concept and functions of JCricket user interface;
- a presentation summarising the technical aspects of JCricket;
- PROVENANCE/CURATION API
The system fetches MARC records – or records in other formats - from the institution for ingestion and BIBFRAME conversion; linked data entities are created from this process and stored in the Cluster Knowledge Base (CKB). In this context, JCricket serves as a transformative tool, enabling librarians with specific authorization levels to refine and enhance the quality of the data. By facilitating human intervention, it acknowledges the inherent limitations of automated processes and harnesses the expertise of librarians to elevate the accuracy and richness of the shared knowledge base.
Within the knowledge base, each cataloger can work on the dataset, using the Provenance to identify their own data. Through the dedicated JCricket web interface, librarians can engage in a spectrum of operations. Key operations include the ability to edit, update, create, delete properties or invalidate clusters.
The JCricket user interface allows librarians to merge multiple clusters into one, addressing cases where different clusters should logically belong to the same entity but were produced as different clusters in automated processes. Conversely, librarians can split a cluster into multiple clusters to rectify cluster reconciliation discrepancies. These edits on entities are saved in the system. Any operation performed on the entity is reported on the Logs page, to have a clear idea of the status of the entity/cluster.
Provenance and Prism
To understand how JCricket operates, the foundational concept of Provenance should be mentioned.
In the LOD Platform, a tenant is represented by a set of institutions contributing to the same Cluster Knowledge Base. An institution within a tenant is called Provenance. We use that term because we always want to retain the relationship between entities and the data that originally contributed to their creation. Each record coming from a Provenance contributes in building/enriching one or more clusters. Therefore, a cluster can be seen as a prism where each facet represents data coming from a given provenance. Each cluster maintains a link to the records it originated from.
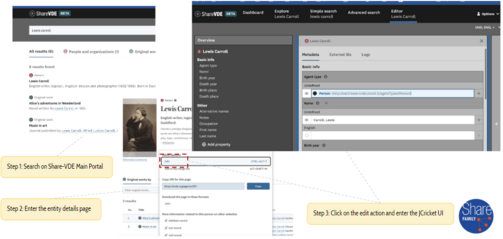
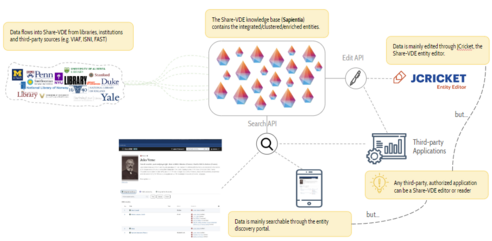
The image below shows a very high-level pictureof JCricket flow, as applied to a LOD Platform tenant with multiple institutions (= Provenances):
- original data flows into the LOD Platform from libraries, institutions and third-party sources (e.g. VIAF, ISNI, FAST);
- the Cluster Knowledge Base contains the integrated/clustered/enriched entities converted to linked data;
- the entity discovery portal (eg. svde.org) shows to end-users the result of this process: data can be searched on the portal;
- data is manually edited through JCricket;
- the entity discovery portal shows the result of manual editing and data curation.
JCricket features recap
- AAA: Authentication + Authorization + Auditing:
- integrated in the discovery portal web interface, for authenticated users;
- user types: basic and advanced.
- Cluster Status API: captures the status of an entity/cluster.
- Edit function:
- real time notifications (through GraphQL subscriptions) about cluster property changes.
- Merge function: C1, C2, C3 => C1, C2, C3
- Multiple phases: create the merge list, edit the merge list, edit clusters, request for review, approve (or deny the merge).
- Split function: C1 => C1, C2
- Multiple phases: create the split-set, edit the split-set, edit clusters, request for review, approve (or deny the split).
- Dictionary API: What are the available cluster types? Which attributes belong to a cluster type? Which relationships? Given an attribute, which is its cardinality? Is it mandatory or not?
- Review workflow: edits are reviewed by advanced editors.
- Entity Event Log: track the history of changes.
- User notifications: for managing the merge/split review lifecycle.
- Data changes synchronization across storages (e.g. RDF Store, Search Engine, RDBMS).
Manual curation - Edit function
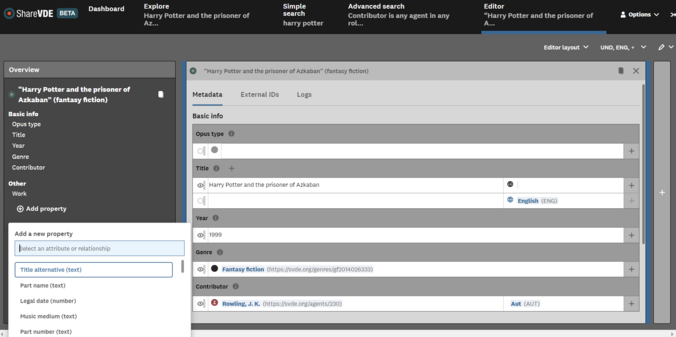
The Edit Cluster operation is available for JCricket editors to add, remove and amend attributes, relationships and links belonging to a single Entity.
If the user is a basic editor, only the properties coming from the user’s provenance will be editable. If the user is an advanced editor, the whole Prism (meaning all properties) will be editable.