No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
The examples have been divided in several subfolders, listed and described as follows. | The examples have been divided in several subfolders, listed and described as follows. | ||
===== REST ===== | =====REST===== | ||
The folder contains the examples related to the REST API. | The folder contains the examples related to the REST API. | ||
====== Content Negotiation ====== | ======Content Negotiation====== | ||
The content negotiation capabilities, as described [[ShareVDEmembers:TechnicalDocumentation/Content Negotiation|in this page]]. Note there are three sub-folders that illustrate the three different ways to negotiate / request a given format. | The content negotiation capabilities, as described [[ShareVDEmembers:TechnicalDocumentation/Content Negotiation|in this page]]. Note there are three sub-folders that illustrate the three different ways to negotiate / request a given format. | ||
====== Provenance API ====== | ======Provenance API====== | ||
ShareVDE entities are the result of merging data coming from several sources. As a consequence of that, an entity provides a set of attributes that have been originally contributed by one or more sources. We call those sources "provenances". | ShareVDE entities are the result of merging data coming from several sources. As a consequence of that, an entity provides a set of attributes that have been originally contributed by one or more sources. We call those sources "provenances". | ||
By means of the Provenance API, the requestor can list the provenances that contributed to a given entity. | By means of the Provenance API, the requestor can list the provenances that contributed to a given entity. | ||
====== Core Entities (e.g. Opus, Work, Instance) ====== | ======Core Entities (e.g. Opus, Work, Instance)====== | ||
There is a folder for each type of entity managed in ShareVDE. API calls have been divided by entity for simplifying and better organising them. | There is a folder for each type of entity managed in ShareVDE. API calls have been divided by entity for simplifying and better organising them. | ||
====== Varia ====== | ======Varia====== | ||
* OpenAPI Specs: the request produces a JSON that can be imported in tools like https://editor.swagger.io/ | *OpenAPI Specs: the request produces a JSON that can be imported in tools like https://editor.swagger.io/ | ||
===== GraphQL ===== | =====GraphQL===== | ||
The folder contains the examples related to the GraphQL API. Each folder includes specific entities; in addition there are two requests that can be used as templates: | The folder contains the examples related to the GraphQL API. Each folder includes specific entities; in addition there are two requests that can be used as templates: | ||
* '''Sample Query Template''': a query example with variables | *'''Sample Query Template''': a query example with variables | ||
* '''Sample Schema Request''': a schema query example | *'''Sample Schema Request''': a schema query example | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
__FORCETOC__ | |||
Revision as of 11:59, 25 November 2021
The following link: https://www.getpostman.com/collections/bd55c075725e90383779 points to a collection of API examples that can be imported in PostMan[1] using the steps described below.
The examples you'll find in the collection target the SIT environment described here.
Install Postman / access Postman web application
Postman is available in several shapes: as a standalone or web application. The interface is pretty similar in both shapes.
You should
- install the application in your machine (not needed if you prefer the web application)
- create an account
- login
Create a workspace
The very first time you log into the application you should create a new workspace. That can be done using the "Workspace" menu item. The workspace can be a team or personal workspace.
Although it is possible to create also a "public" workspace, at this stage we don't recommend to create that for hosting the Share VDE API calls.
Import the sample collection
Once the workspace has been created click on the "Import" link that appears on the top of the explorer panel
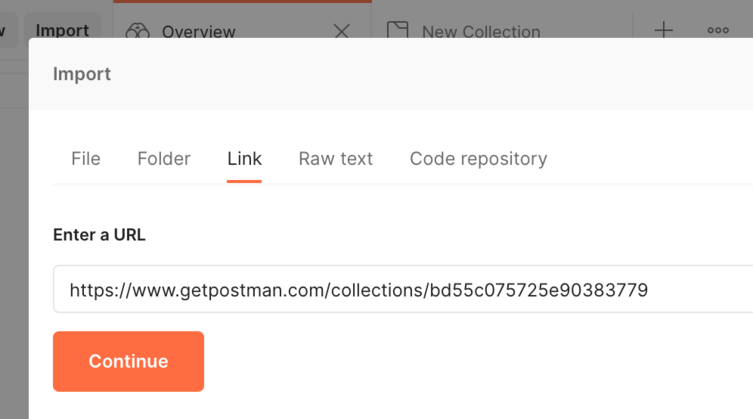
The import dialog should appear. You need to select the "Links" tab and put this link https://www.getpostman.com/collections/bd55c075725e90383779 in the text box, as illustrated in the following picture.
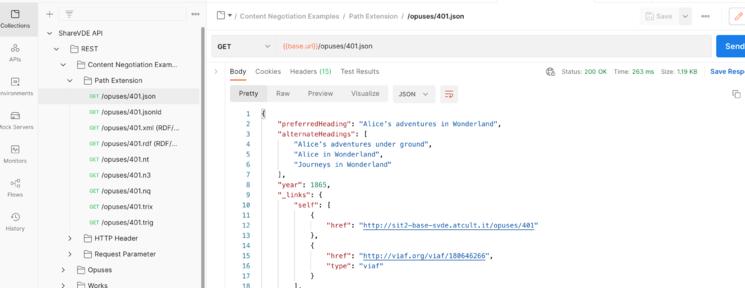
Once confirmed, in the left explorer pane you should see the examples. Just click on one of them and it executes the request, including the authentication workflow.
Collection overview
The examples have been divided in several subfolders, listed and described as follows.
REST
The folder contains the examples related to the REST API.
Content Negotiation
The content negotiation capabilities, as described in this page. Note there are three sub-folders that illustrate the three different ways to negotiate / request a given format.
Provenance API
ShareVDE entities are the result of merging data coming from several sources. As a consequence of that, an entity provides a set of attributes that have been originally contributed by one or more sources. We call those sources "provenances".
By means of the Provenance API, the requestor can list the provenances that contributed to a given entity.
Core Entities (e.g. Opus, Work, Instance)
There is a folder for each type of entity managed in ShareVDE. API calls have been divided by entity for simplifying and better organising them.
Varia
- OpenAPI Specs: the request produces a JSON that can be imported in tools like https://editor.swagger.io/
GraphQL
The folder contains the examples related to the GraphQL API. Each folder includes specific entities; in addition there are two requests that can be used as templates:
- Sample Query Template: a query example with variables
- Sample Schema Request: a schema query example
- ↑ https://www.postman.com